The Beach Ball Cure For Market Volatility
Submitted by Silverlight Asset Management, LLC on March 27th, 2019
Do you ever feel like your portfolio is a beach ball randomly bouncing around a stadium?
If that describes your recent experience, it’s easy to understand why. The S&P 500 was down over 13% last quarter. Now the index has staged a monster rally this quarter—bouncing back by 13%. Why such a dramatic reversal?
Markets consist of millions of people, making millions of decisions, for millions of reasons. It’s hard to pinpoint causality.
Some say the V-shaped recovery is due to the Fed pivoting dovish. Others cite relaxing trade tensions. Then there are strategists, like Marko Kolanovic at JPMorgan, who attribute the steep moves to low liquidity levels in the market.
One thing we know for sure—investors who sold in December just got whipsawed. Badly.
Whether you're a market pro or Average Joe, it takes discipline to successfully navigate the market. If things like ‘market liquidity’ are a foreign concept, here's a simple metaphor that may help your decision-making process.
A Simple Reason Stocks Go Up
Picture what happens to a beach ball pushed into liquid. The air in the ball pressures it back up, right?
If you understand how dividend compounding works, you can engineer similar physics to improve the buoyancy of your portfolio.
The most straightforward explanation I've found for why stocks rise over time comes from Lowell Miller's book, The Single Best Investment: Creating Wealth with Dividend Growth.
Miller argues that as asset classes compete with one another for investors' capital, money flows to where it's treated best; i.e. the best risk-adjusted yield.
Bonds usually pay a fixed sum. So if you buy a bond at a certain yield and hold it to maturity, you get the yield you paid for upfront.
Stock dividends, on the other hand, often rise over time—i.e. you get more than the starting yield. The growth component is the main reason why stocks trounce bonds and cash over the long-term. Reinvested dividends create a compounding machine.
To better illustrate, here's an example.
I own shares in biotech behemoth, Amgen (ticker: AMGN). The company provides supportive-care products to kidney disease and cancer patients. Prudent cost-management has enabled Amgen's free cash flow as a percentage of sales to hover around 40%, which is excellent compared to most firms.
Amgen distributes a lot of that cash to shareholders via stock buybacks and dividends. This year, AMGN should pay $5.80 in dividends; equivalent to a 3.2% yield. Over the next three years, my dividend growth model projects the dividend to rise about 10% annually. If you think that seems overly aggressive, consider Amgen's quarterly dividends grew at a 22% annual pace over the last five years.
In the table below, I extrapolate my 10% growth rate estimate out over 12 years. Look at what happens to the dividend yield and pay special attention to the later years.
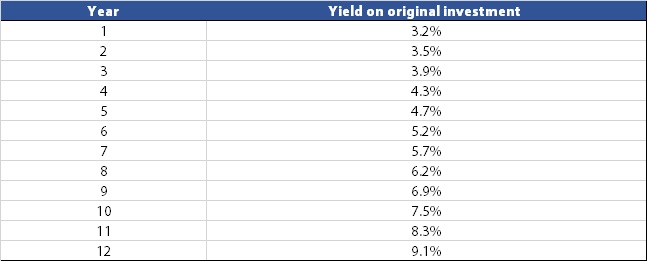
AMGN est. dividend yield. Data source: Bloomberg.
If someone invests today in AMGN, they can only venture a guess where the stock price will be in 12-months. But since the firm has a strong balance sheet and diverse pipeline, they can be reasonably confident the dividend is secure.
Imagine what happens if AMGN shares go nowhere for a prolonged period. Assuming the dividend grows, investors will eventually be attracted to the yield profile. It will become a magnet for capital and the shares will be bid higher. Dividend growth promotes stock price growth.
What about when market corrections come along? This is where dividend stocks benefit from a buoyancy effect. The lower their share price, the higher the dividend yield. Eventually, enough investors will be attracted to the rising yield to halt the stock's decline.
I consider high-quality dividend growth stocks: "The Beach Ball Cure For Market Volatility." Whatever market mayhem occurs, you can rest easy when you're confident dividends create a reliable floor.
Rolling returns give the best picture for how stocks perform over both good and bad times. Looking through that prism, it's evident that the longer you stay invested in the equity market, the better your probability of making money.
Reviewing over 146 years of return history, we learn:
- In a single year, the chance of losing money is about 1-in-3.
- Over 5 and 10-year holding periods, the frequency of losses shrinks considerably.
- Over any 20-year rolling period, U.S. stocks have never lost money.
If market volatility stresses you, try putting on noise canceling headphones. Focus on fundamentals. Pump up your portfolio with dividend growth stocks and let it float you to a higher net worth.
*Also published by Forbes. Reprinted with permission.
This material is not intended to be relied upon as a forecast, research or investment advice. The opinions expressed are as of the date indicated and may change as subsequent conditions vary. The information and opinions contained in this post are derived from proprietary and nonproprietary sources deemed by Silverlight Asset Management LLC to be reliable, are not necessarily all-inclusive and are not guaranteed as to accuracy. As such, no warranty of accuracy or reliability is given and no responsibility arising in any other way for errors and omissions (including responsibility to any person by reason of negligence) is accepted by Silverlight Asset Management LLC, its officers, employees or agents. This post may contain “forward-looking” information that is not purely historical in nature. Such information may include, among other things, projections and forecasts. There is no guarantee that any of these views will come to pass. Reliance upon information in this post is at the sole discretion of the reader.
Testimonials Content Block
More Than an Investment Manager—A Trusted Guide to Financial Growth
"I’ve had the great pleasure of having Michael as my investment manager for the past several years. In fact, he is way more than that. He is a trusted guide who coaches his clients to look first at life’s bigger picture and then align their financial decisions to support where they want to go. Michael and his firm take a unique and personal coaching approach that has really resonated for me and helped me to reflect upon my core values and aspirations throughout my investment journey.
Michael’s focus on guiding the "why" behind my financial decisions has been invaluable to me in helping to create a meaningful strategy that has supported both my short-term goals and my long-term dreams. He listens deeply, responds thoughtfully, and engages in a way that has made my investment decisions intentional and personally empowering. With Michael, it’s not just about numbers—it’s about crafting a story of financial growth that has truly supports the life I want to live."
-Karen W.
Beyond financial guidance!
"As a long-term client of Silverlight, I’ve experienced not only market-beating returns but also invaluable coaching and support. Their guidance goes beyond finances—helping me grow, make smarter decisions, and build a life I truly love. Silverlight isn’t just about wealth management; they’re invested in helping me secure my success & future legacy!"
-Chris B.
All You Need Know to Win
“You likely can’t run a four-minute mile but Michael’s new book parses all you need know to win the workaday retirement race. Readable, authoritative, and thorough, you’ll want to spend a lot more than four minutes with it.”
-Ken Fisher
Founder, Executive Chairman and Co-CIO, Fisher Investments
New York Times Bestselling Author and Global Columnist.
Packed with Investment Wisdom
“The sooner you embark on The Four-Minute Retirement Plan, the sooner you’ll start heading in the right direction. This fun, practical, and thoughtful book is packed with investment wisdom; investors of all ages should read it now.”
-Joel Greenblatt
Managing Principal, Gotham Asset Management;
New York Times bestselling author, The Little Book That Beats the Market
Great Full Cycle Investing
“In order to preserve and protect your pile of hard-earned capital, you need to be coached by pros like Michael. He has both the experience and performance in The Game to prove it. This is a great Full Cycle Investing #process book!”
-Keith McCullough
Chief Executive Officer, Hedgeye Risk Management
Author, Diary of a Hedge Fund Manager
Clear Guidance...Essential Reading
“The Four-Minute Retirement Plan masterfully distills the wisdom and experience Michael acquired through years of highly successful wealth management into a concise and actionable plan that can be implemented by everyone. With its clear guidance, hands-on approach, and empowering message, this book is essential reading for anyone who wants to take control of their finances and secure a prosperous future.”
-Vincent Deluard
Director of Global Macro Strategy, StoneX

